Beyond Binary: The Environmental, Technological, and Social Catalysts behind the Transgender Wave
The recent, undeniable upswing in the visibility and recognition of transgender identities has sparked riveting conversations about the potential catalysts fueling this perceived expansion. Five groundbreaking hypotheses have emerged, each reshaping our understanding of the origins of transgender identities in a distinctly disruptive and futuristic light: the environmental prevalence of endocrine disruptors, the rise of radical transhumanism, the viral-like spread of social contagion, an evolutionary response to overpopulation, and a fascinating look at the implications of quantum reality theory.
The initial hypothesis shines a light on the potentially game-changing influence of omnipresent endocrine-disrupting chemicals (EDCs). These stealth disruptors lurk in our environment, hiding in everyday items such as food packaging, cosmetics, and plastics, subtly meddling with our hormonal systems. Research has peeled back the curtain on their power to mimic or block hormones and wreak havoc on the body's normal functions. Their most potent potential impact? Influencing brain development and behavior. This has ignited a debate on whether the rising tide of EDCs in our environment could be the unseen hand shaping gender identity and fueling the apparent increase in transgender individuals.
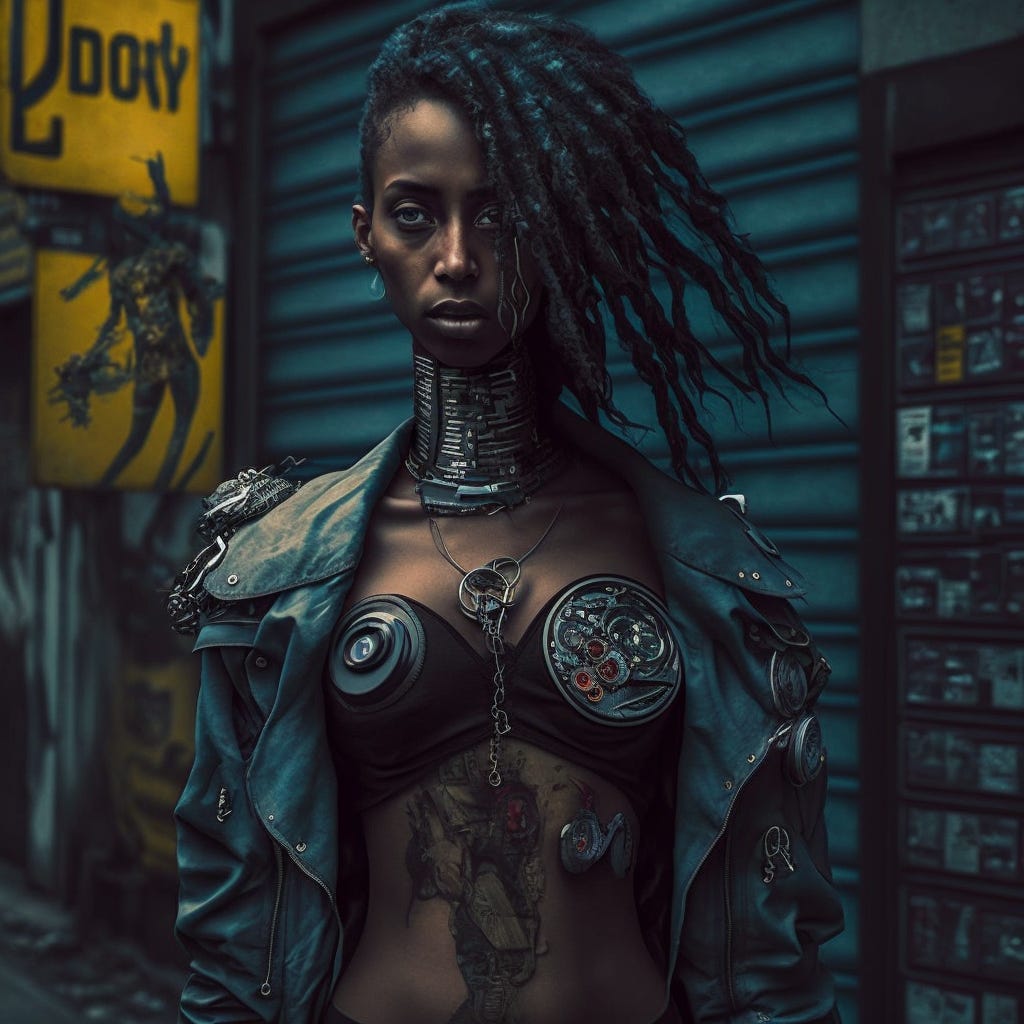
The second hypothesis turns to the burgeoning frontier of transhumanism. This progressive intellectual and cultural movement champions the use of cutting-edge technology to supercharge human intellectual, physical, and psychological capacities. As we shatter the boundaries of technological capabilities, with biohacking and body modifications becoming the norm, we're nurturing an environment that embraces the transcendence of biological limitations. This shift towards accepting and even celebrating transhumanism could be laying the groundwork for individuals to explore and express their gender identities more freely, potentially fueling the perceived growth in transgender identities.
The third theory, commonly termed the social contagion theory, proposes a contagion-like spread of transgender identities. It suggests that the concept of being transgender is spreading through society at an unprecedented pace, propagated via social networks, media, and peer influence in a manner akin to a viral outbreak. This provocative theory suggests that individuals, especially the young and impressionable, could be influenced or even 'infected' by exposure to these influences, leading them to identify as transgender.
The fourth theory, while unarguably speculative, dives into a realm that marries biology and sociology, exploring the tantalizing prospect that the swell in transgender identities might be evolution's unconventional antidote to global overpopulation. This theory suggests nature's masterstroke lies in promoting a seismic shift in reproductive roles and sexual behavior, leading to an unparalleled diversity as a biological control valve for booming population numbers. In this brave new world, the emergence of more individuals identifying as transgender could be an audacious evolutionary gambit aimed at sustaining balance in an increasingly teeming, crowded global village.
Meanwhile, the fifth theory propels us into the fringe of quantum realities, a space where the traditional and tangible yield to the abstract and infinitely possible. This audacious theory proposes that the explosion in transgender identities is a manifestation of a quantum reality, where multiple realities, each with its unique version of truth, coexist in an intricate cosmic dance. This revolutionary perspective posits that individuals are capable of perceiving and embodying different gender identities across these parallel realities. This suggests an entirely new dimension to understanding the rise in transgender identities, offering a thought-provoking, if disruptive, explanation that challenges our conventional perception of identity and reality.
In conclusion, the accelerated recognition and visibility of transgender individuals in our society demands a fresh, futuristic exploration of the possible drivers behind this perceived growth. The provocative theories of ubiquitous environmental triggers like endocrine-disrupting chemicals, the empowering rise of transhumanism, the viral-like spread via social contagion theory, an evolutionary response to overpopulation, and a quantum reality theory all offer groundbreaking perspectives, even though they remain speculative. It's time to embrace these disruptive ideas, for they might hold the key to understanding the ever-evolving landscape of gender identity.